SZTE Nanotechnological Research Group
Principal investigator: Dr. Rita Ambrus habil PhD
SmartCrystals® for efficient dissolution enhancement of poorly water-soluble drugs
SmartCrystals® for efficient dissolution enhancement of poorly water-soluble drugs
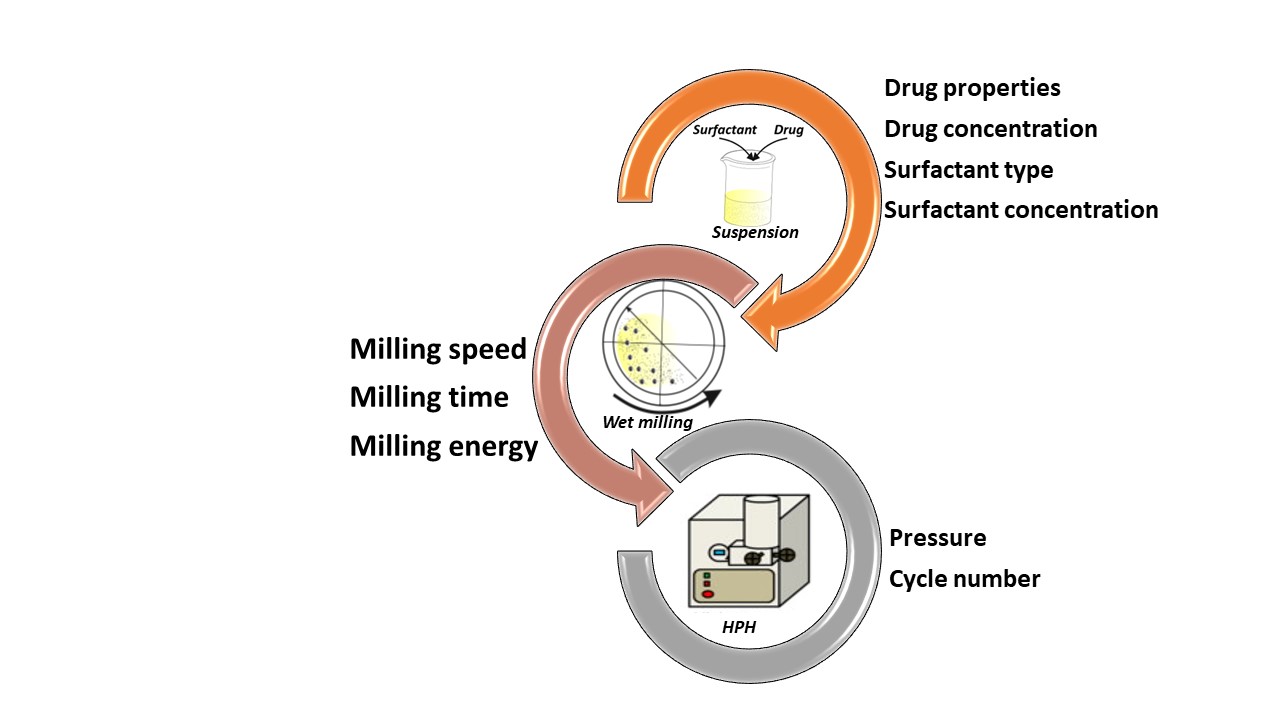
Nanosization is one of the most applied technologies used to improve the dissolution rate of poorly water-soluble drugs. Combination technology (CT) has also been developed as a new method to prepare nanocrystals. CT combines wet bead milling and high pressure homogenization (HPH) can maximize particle reduction for faster dissolution . Besides, overcome the limitations of the single methods [1]. The main merit of nanocrystals is that they remain crystalline structure during particle size reduction, so that stable nanosuspensions can be prepared, e.g. intravenous injection of nanosuspension, could dissolve in 5 minutes, but the crystals themselves can pass through the BBB with the help of Trojan macrophages, thus targeting the brain.
This project aims to investigate the feasibility of nanocrystals preparation of different active pharmaceutical ingredients. Two non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs -meloxicam and niflumic acid- are subjected to the present investigation. The two drugs belong to class II of the biopharmaceutical classification systems considering their low solubility and high permeability. These drugs also have limited solubility in the most common organic solvents [2,3] (but they have improved solubility at higher pH).
Parameters of critical effects on the physicochemical properties of the nanocrystals must be defined, and cautiously controlled. Surfactant type and concentration, drug concentration, milling time, milling speed, and pressure and cycle number of the high-pressure homogenizer are examples of critical material and process parameters of high impacts. Moreover, the influences of the drying method and excipients like cryoprotectants must be evaluated.
The characterization of nanocrystals involves:
1. Particle size, polydispersity index, and zeta potentials (Zeta-sizer).
2. Morphology (Scanning electron microscopy).
3. Thermal behaviors (Differential scanning calorimetry).
4. Structural analysis (X-ray diffractometer, Fourier transform infra-red spect.).
5. In vitro dissolution studies in different media.
6. In vivo studies
References:
1. Möschwitzer J, Müller RH. New method for the effective production of ultrafine drug nanocrystals. Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology. 2006;6(9–10):3145–53.
2. Romero S, Escalera B, Bustamante P. Solubility behavior of polymorphs I and II of mefenamic acid in solvent mixtures. International Journal of Pharmaceutics. 1999;178(2):193–202.
3. Systems L, Soluble L, Janakidevi S, Pradesh A. Solubility Enhancement of Meloxicam By Liquisolid Technique and Its. 2015;6(2):835–40.

